Ptosis - Eyelids that Droop
New York City Ptosis Treatment Dr. Brian Brazzo
What is ptosis?
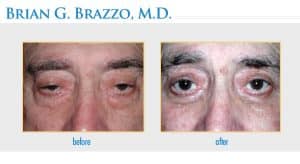 Ptosis is the medical term for drooping upper eyelids. This condition may affect one or both upper eyelids. When the eyelid descends, it may block the upper field of vision. Ptosis may be mild, in which case the lid partially covers the pupil, or it may be severe, in which the lid completely covers the pupil and obscures all vision. Ptosis that is present from birth is called congenital ptosis.
Ptosis is the medical term for drooping upper eyelids. This condition may affect one or both upper eyelids. When the eyelid descends, it may block the upper field of vision. Ptosis may be mild, in which case the lid partially covers the pupil, or it may be severe, in which the lid completely covers the pupil and obscures all vision. Ptosis that is present from birth is called congenital ptosis.
What are the causes?
In children, the most common cause is improper development of the levator muscle, that is the primary muscle that lifts the upper eyelid. In adults, ptosis may occur as a result of aging, trauma, or muscular or neurological disorders.
The tendon that attaches the levator muscle to the eyelid stretches over time, resulting in a low eyelid position which covers part of the eye. It is very common for people to develop ptosis as years progress. It is more common after trauma or eye surgery, including cataract surgery.
What are the symptoms?
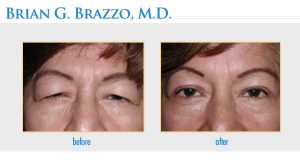 People who have ptosis often have difficulty keeping the eyes open. Other common problems include eyestrain and headaches from the increased effort needed to raise the eyelids. The eyes often become fatigued particularly when reading. In severe cases, it may be necessary to tilt your head back or lift the eyelids with your finger in order to see out from under the drooping eyelid.
People who have ptosis often have difficulty keeping the eyes open. Other common problems include eyestrain and headaches from the increased effort needed to raise the eyelids. The eyes often become fatigued particularly when reading. In severe cases, it may be necessary to tilt your head back or lift the eyelids with your finger in order to see out from under the drooping eyelid.
Are there other conditions associated with ptosis?
Children with ptosis may also have a lazy eye, which is also known as amblyopia. In adults, ptosis may be the first sign of myasthenia gravis, a disorder in which the muscles become weak and tire very easily. Ptosis may also be present in numerous other neurological conditions.
What are the treatments?
Congenital ptosis is treated surgically and the operation is determined on the basis of the severity of the ptosis and the strength of the levator muscle. In adults, nearly all ptosis surgeries involve tightening or reattaching the levator muscle to its proper location. The goal of ptosis surgery is to elevate the upper eyelid to improve vision and obtain an excellent appearance of the eyes and eyelids. Ptosis surgery is usually performed in the office under local anesthesia. In some conditions, it needs to be performed in the hospital with intravenous sedation.
What are the risks and complications?
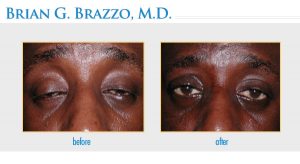 Following the procedure, there is minor bruising and swelling of the eyelid which lasts for up to one week. The incision is placed in the normal eyelid crease and therefore tends not to be noticed after the healing takes place. Dr. Brazzo always places absorbable sutures, so the sutures do not need to be removed after surgery. Bleeding and infection are very uncommon; discomfort is minimal and is usually managed with one dose of Tylenol on the evening after the surgery.
Following the procedure, there is minor bruising and swelling of the eyelid which lasts for up to one week. The incision is placed in the normal eyelid crease and therefore tends not to be noticed after the healing takes place. Dr. Brazzo always places absorbable sutures, so the sutures do not need to be removed after surgery. Bleeding and infection are very uncommon; discomfort is minimal and is usually managed with one dose of Tylenol on the evening after the surgery.
Who performs the surgery?
Dr. Brazzo has extensive training in ophthalmic plastic surgery and is a qualified oculoplastic surgeon. He is one of a small group of physicians in this country who is trained specifically to do this type of surgery. Dr. Brazzo has completed several thousand ptosis repairs. He has written books and lectured other doctors and residents around the country on the most recent advances.
Over the years, Dr. Brazzo has treated many blepharoplasty New York City patients looking to rejuvenate the area around the eyes. He is also respected among Restylane, Juvederm and Botox New York City patients seeking non-surgical cosmetic treatments. NYC Latisse patients come to Dr. Brazzo to obtain this leading-edge product that promotes the growth of naturally fuller, longer and thicker lashes.
